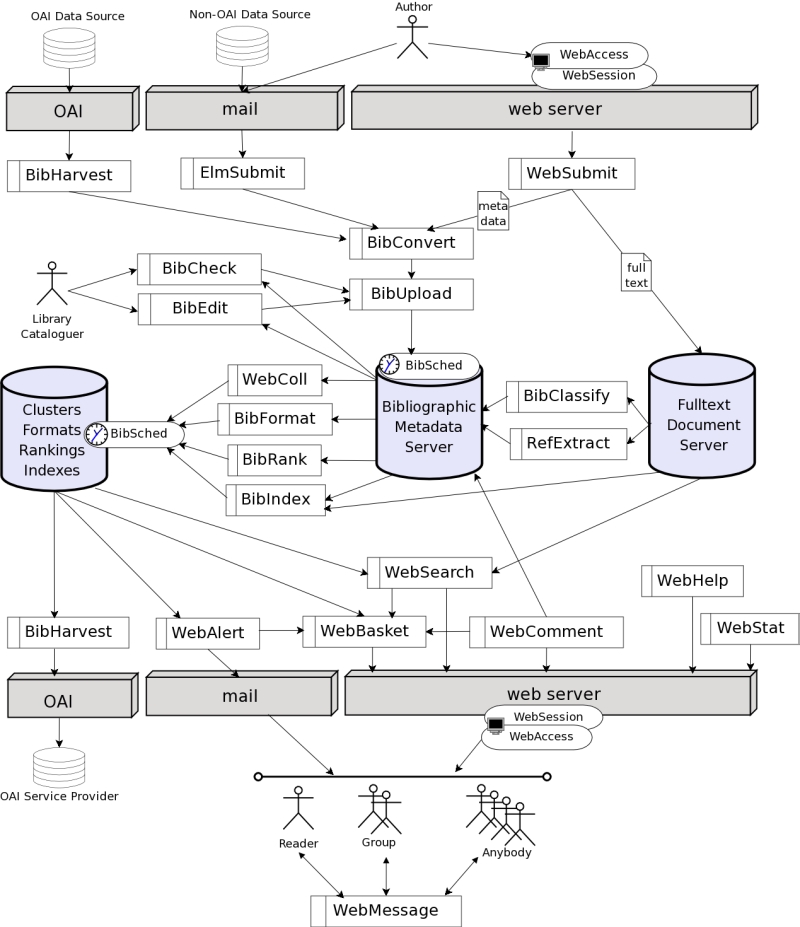
Modules Overview
Invenio consists of several more or less independent modules with
precisely defined functionality. The general criterion for module
names is to use the ``Bib'' prefix to denote modules that work more
with the bibliographic data, and the ``Web'' prefix to denote modules
that work more with the Web interface. (The difference is of course
blurred in some cases, as in the case of search engine that has got a
web interface but searches bibliographic data.)
Follows a brief description of what each module does. After
descriptions the module relationship diagram is presented.
- BibCheck permits administrators and library
cataloguers to automate various kind of tests on the metadata to see
whether the metadata comply with quality standards. For example,
that certain metadata fields are of a certain length, that they have
numeric content, that they must not be present when other field
exists, that their content is governed by an authority base depending
on values of other fields, etc. The module can report its findings
or can even automatically correct some kind of errors. (FIXME: not
included in CVS yet.)
- BibClassify allows automatic extraction of
keywords from fulltext documents, based on the frequency of specific
terms, taken from a controlled vocabulary. Controlled vocabularies
can be expressed as simple text thesauri or as structured, RDF-compliant,
taxonomies, to allow a semantic classification.
- BibConvert allows metadata conversion from any
structured or semi-structured proprietary format into any other
format, typically the MARC XML that is
natively used in Invenio. Nevertheless the input and output formats
are fully configurable and have been tested on data importations from
more than one hundred data sources. The power of this utility lies in
the fact that no structural attributes of data source are presumed,
but they are defined in an extensive data source
configuration. Inevitably, this leads to a high complexity of the
BibConvert configuration language. Most frequent configurations are
provided with the Invenio distribution, such as a sample
configuration from Qualified Dublin Core into the MARCXML.
In general the BibConvert configuration consists from the source
data descriptions and target data descriptions. The processor then
analyzes and parses the input data and creates the resulting data
structure, similarly as the XSLT processor would do. Typically the
BibConvert is aimed at usage for input data that do not dispose of an
XML representation. The source data is required to be structured or
semi-structured, (i.e. not expressed in natural language that is a
subject of information extraction task) and its processing involves
several steps including record separation and field extraction upto
transformation of source field values and their formatting.
- BibEdit permits one to edit the metadata via a
Web interface.
- BibFormat is in charge of formatting the
bibliographic metadata in numerous ways. This truly enables the
separation of data content administration and formatting layout.
BibFormat can act in the background and format the records when
needed, or can preformat records for some often used outputs, such as the
brief format used when displaying search results.
The BibFormat settings can be administered either through a
user-friendly web interface, or directly by editing human-readable
configuration files.
- OAIHarvest represents the OAi-PMH compatible harvester
allowing the repository to gather metadata from fellow OAi-compliant
repositories and the OAi-PMH repository management. Repository is
built directly on top of the database and disposes of an OAi
repository manager that allows to perform the administrative tasks on
the repository aside from the principal generic data administration
module. The database can be partially or completely open for
harvesting in the scope of the OAi-PMH protocol. In this case, all
data is provided in raw form, where the semantics of individual tags
is indicated uniquely by the MARC21 naming convention. This is
particularly interesting for institutes that are specialized in
cross-archive and cross-disciplinary services provision, as for
example the ARC service provider.
- BibIndex module takes care of the indexation of
metadata, references and full text files. Two kinds of indexes --
word and phrase index -- are being maintained. The user can define
several logical indexes (e.g. author index, title index, etc.) and
the correspondence of which physical MARC21 metadata tag goes into
which logical field index. An index consists of two parts: (i) a
forward index listing various words (or phrases) found in the given
field, with the set of record identifiers where the given word can be
found; and (ii) a reverse index listing record identifiers, with the
set of words of the given record that go to the forward index. Such
a two-part indexing technique allows one to rapidly update only those
words that have changed in the input metadata record. The indexes
were designed with the aim to provide fast user-response search times
and are faster than native MySQL (full text) indexes.
- BibMatch permits to filter input XML files
against the database content, attempting to match records via certain
criteria, for example to avoid doubly-inputted records.
- BibRank permits to set up various ranking
criteria that will be used later by the search engine. For example,
ranking by the word frequency, or by some metadata tag value such as
journal name by means of the journal impact factor knowledge base, or
even by the number of downloads of a particular paper. Note that
BibRank is independent of BibIndex.
- BibSched The bibliographic task scheduler is
central unit of the system that allows all other modules to access
the bibliographic database in a controlled manner, preventing sharing
violation threats and assuring the coherent execution of the database
update tasks. The module comes with an administrative interface that
allows to monitor the task queue including various possibilities of a
manual intervention, for example to re-schedule queued tasks, change
the task order, etc.
- BibUpload allows to load the new bibliographic
data into the database. To effectuate this task the data must be a
well-formed XML file that complies with the current metadata tag
selection schema. Usually, the properly structured input files of
BibUpload come from the BibConvert utility.
- ElmSubmit is an email submission gateway that
permits for automatic document uploads from trusted sources via
email. (Usually web submission or harvesting is preferred.)
- MiscUtil is a collection of miscellaneous
utilities that other modules are using, like the international
messages, etc.
- WebAccess module is responsible for granting
access to users for performing various actions within the system. A
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) technique is used, where users
belong to several groups according to their role in the system. Each
user group can be granted to perform certain actions depending on
possible one more action arguments. WebAccess is presently used
mainly for the administrative interface. There are basically two
kinds of actions: (i) configuration of administrative modules and
(ii) running administrative tasks.
- WebAlert module allows the end user to be
alerted whenever a new document matching her personal criteria is
inserted into the database. The criteria correspond to a typical
user query as if it would be done via the search interface. For
example, a user may want to get notified whenever a new document
containing certain words, or of a certain subject, is inserted. A
user may create several alerts with a daily, weekly, or a monthly
frequency. The results of alert searches are either sent back to the
user by email or can also be stored into her baskets.
- WebBasket module enables the end user of the
system to store the documents she is interested in in a personal
basket or a personal shelf. The concept is similar to popular
shopping carts. One user may own several baskets. A basket can be
either private or public, allowing a simple document sharing
mechanism within a group.
- WebComment provides a community-oriented tool to
rank documents by the readers or to share comments on the documents
by the readers. Integrated with the group-aware WebBasket, WebGroup,
WebMessage tools, WebComment is at the heart of the social network
features of the Invenio software.
- WebHelp presents some global user-level,
admin-level, and hacker-level documenation on Invenio. The
module-specific documentation is included within each particular
module.
- WebMessage permits the communication between
(possibly anonymous) end users via web message boards, to invite
readers to join the groups, etc.
- WebSearch module handles user requests to search
for a certain words or phrases in the database. Two types of
searching can be performed: a word search or a phrase search. The
system allows for complex boolean queries, regular expression
searching, or a combined metadata, references and full text file
searching in one go. Users have a possibility to browse for present
index terms. If no direct match could have been found with the
user-typed query pattern, the system proposes alternative matches as
a search guidance. The search indexes were designed to provide fast
response times for middle-sized data collections of up to 106
records.
The metadata corpus is organized into metadata collections that
are directly accessible through the browse function, similarly to the
popular concept of Web Directories. Orthogonal views on the document
corpus are enabled in the search interface via a concept of virtual
collections: for example, a document may be classified both according
to its type (e.g. preprint, book) and according to its Dewey decimal
classification number. Such a flexible organization views allows for
the creation of easy navigation schemata to the end users.
- WebSession is a session and user management
module that permits to differentiate between users. Useful for
personalization of the interface and services like personal baskets
and alerts.
- WebStat is a configurable system that permits to
gather statistics about the health of the server, the usage of the
system, as well as about some particular system features.
- WebStyle is a library of design-related modules
that defines look and feel of Invenio pages.
- WebSubmit is a comprehensive submission system
allowing authorized individuals (authors, secretaries and repository
maintenance staff) to submit individual documents into the
system. The submission system disposes of a flow-control mechanism
that assures the data approval by authorized units. In total there
are several different exploitable submission schemas at a disposal,
including an automated full text document conversion from various
textual and image formats. This module also disposes of information
extraction functionality, focusing on bibliographic entities such as
references, authors, keywords or other implicit metadata.
Relationship between the modules: